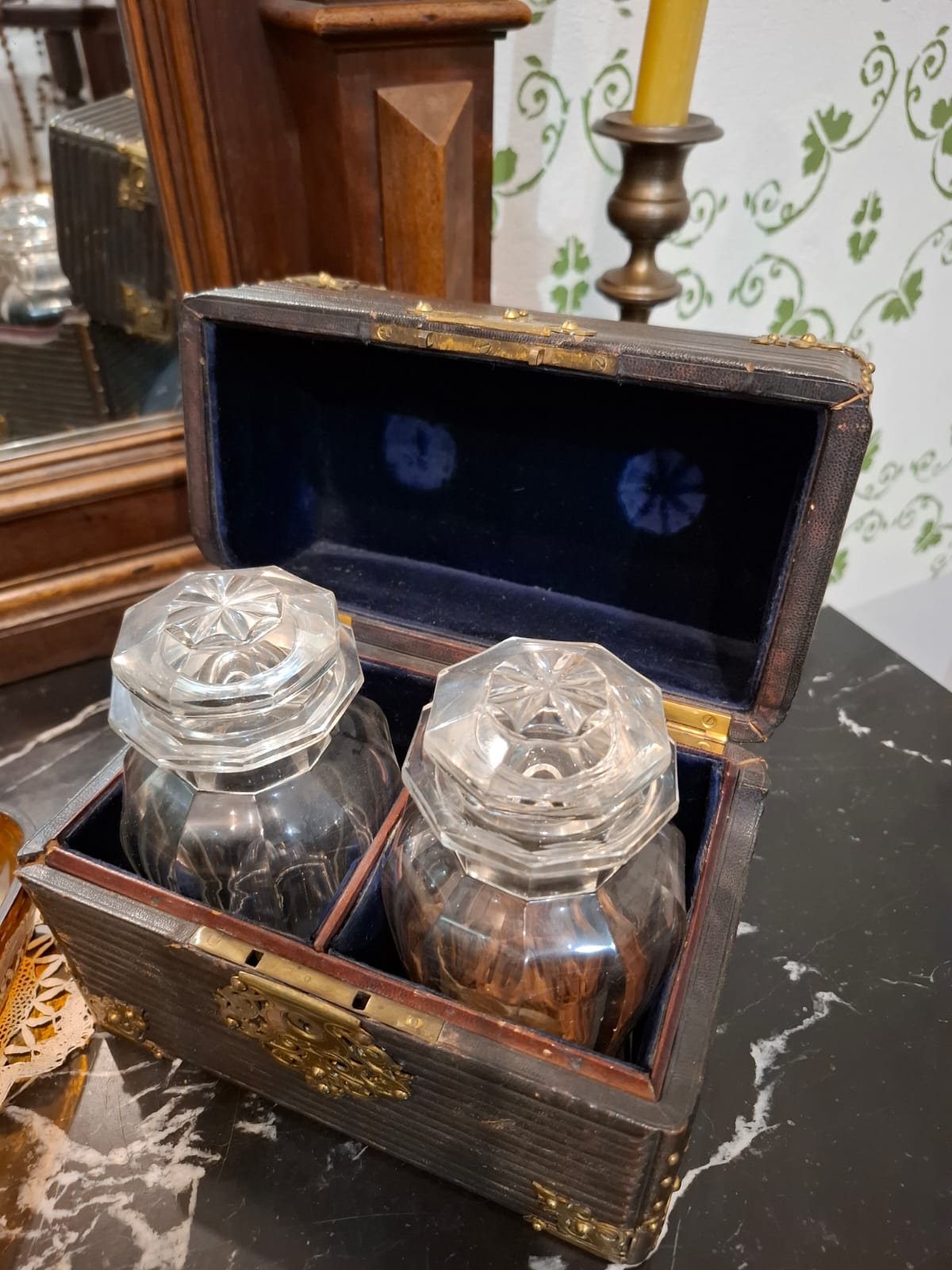Various types of perfumes were known in ancient times. Glass perfume bottles were found during excavations in Egypt. They were also known in other ancient countries and were not forgotten in Arab countries. They were revived in Europe in the Middle Ages, and from the Renaissance onward, they began to gain increasing popularity and importance. Primarily because of their scent, which not only brought pleasure but also masked various unpleasant odors common at the time. Perfumes are based on aromatic substances, primarily oils, fragrance fixatives, and solvents, primarily alcohols, which formed the basis of liquid fragrances. The use of alcohol, with its disinfecting properties, imparted similar characteristics to perfumes, although their users were likely unaware of this. For centuries, natural fragrances, primarily floral essential oils, were used. Perfume production was the preserve of specialized artisans, but scented waters, based on a similar principle to tinctures, were also produced at home. They were cheaper, but also not as durable as professional products. Due to their price, perfumes were usually stored in small containers, unlike various types of eau de parfum. One example is a lidded chest containing two large glass bottles with stoppers, placed in matching compartments. It is unclear whether these are perfumery products or homemade, but they contain preserved lily flowers in an alcoholic brine.
A Travel Case with Perfume Bottles